The semantic model in Xpert Analytics Cloud provides rich role & access control functions to ensure the security and access control of data. These role permissions can be applied to multi-dimensional data sets, dimensions, hierarchies, and members to meet specific user needs.
In the Xpert Analytics Cloud, two types of roles can be created: single role and composite role.
Single role: A single role is an independent role with specific permissions. Permissions to access multidimensional datasets, dimensions, levels, and members can be specified for a single role. This way, you can control the role's access to and manipulation of different levels in the data model.
Composite role: Composite roles are roles composed of multiple single roles. For example, a composite role can be created for a regional manager to allow access to a union of sub-regions in the sales dataset.
Through these role permission control functions, Xpert Analytics Cloud provides flexible 🔐 Access Control mechanism, so that administrators can accurately manage the access permissions of data according to user roles and needs. This not only protects the security of sensitive data, but also ensures the compliance and privacy protection of data.
Roles Design
Next, we will create example roles for the AdventureWorks Sales dataset to demonstrate the role-based permissions control feature of the Xpert Analytics Cloud semantic model. In the previous article, "Sample: AdventureWorks Sales - 1. Modeling" we created the AdventureWorks Sales multidimensional dataset, which includes the following dimensions:
- Reseller
- Customer
- Sales Territory
- Date
- Product
- Sales Order
And the following measures:
- Order Quantity
- Sales Amount
- Total Product Cost
- Unit Price
- Profit
First, we will create four examples of individual roles for the Sales dataset:
Sales Manager:
- Has full access to the Sales dataset, allowing them to view detailed information such as sales orders and product sales.
- Can access all dimensions, including time, region, and product, for comprehensive sales analysis and reporting.
Regional Sales Manager:
- Can access a portion of the Sales dataset, limited to sales data within specific regions.
- Can view and analyze sales trends, customer behavior, and other data specific to certain regions.
Product Manager:
- Has full access to the Sales dataset except for the Customer dimension, focusing only on product-related information.
- Can view product sales, product categories, product attributes, and perform product analysis and comparisons.
Sales Representative:
- Has limited access rights and can only view and analyze customer information relevant to themselves.
- Can view individual sales performance, customer feedback, order statuses, etc., for tracking and managing their own sales activities.
Next, we will create corresponding role definitions for these roles within the system.
Creating Standard Roles
Sales Manager
The Sales Manager role has full access to the Sales dataset. We will create a standard role named "Sales Manager" and assign it full access to the Sales dataset.
- Role Overview
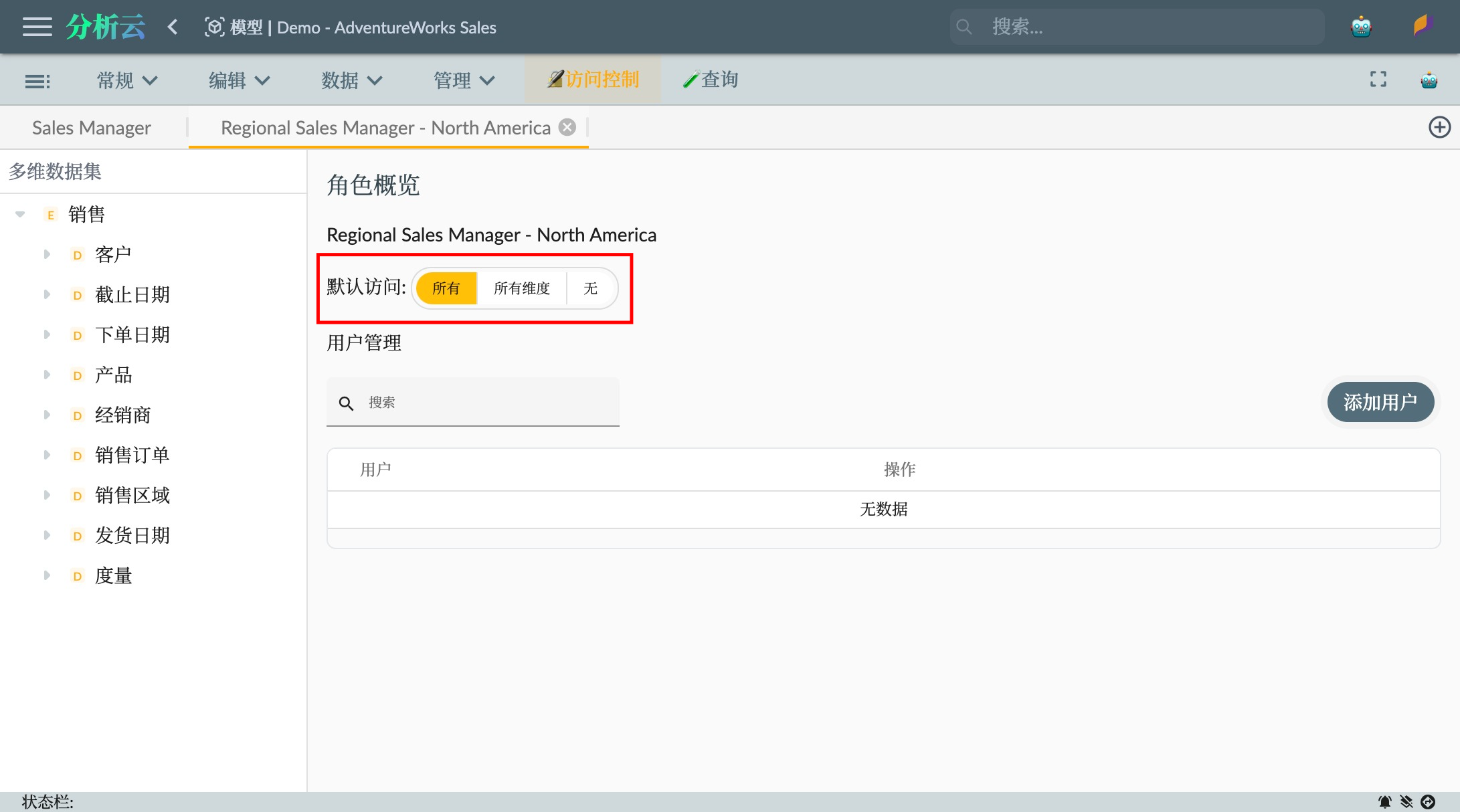
- Default Access: All, including all dimensions and the multidimensional dataset.
- Users: User accounts assigned to the Sales Manager role.
- Multidimensional Dataset: Sales
- Default Access: All, including all dimensions and measures.
The semantic model administrator can add users and assign roles to them in the role overview interface. Users can also be assigned roles through user management in the access control overview interface.
Regional Sales Manager
The Regional Sales Manager's access is limited to sales data within specific regions. We will differentiate between different Regional Sales Manager roles using the Sales Territory dimension members of the Sales dataset.
For example, we create two roles for Regional Sales Managers:
- Regional Sales Manager - North America
- Regional Sales Manager - Europe
As shown in the following image, we create a standard role for the Regional Sales Manager - North America. The role's default access permission is set to All, which means all dimensions except for specific restricted sales territory members can be freely accessed.
We add the Sales multidimensional dataset to this role and go to the role settings interface for this dataset. We set the following properties:
- Default Access: All, allowing access to all dimensions except for specific restricted sales territory members.
Then, we add a restriction to the role by setting a dimension restriction on the Sales Territory dimension members. We drag the Sales Territory dimension to the right area to add the dimension restriction and configure the dimension's permissions as follows:
- Aggregation Policy: Hidden, meaning that access to overall data outside of the allowed members is prohibited.
- Default Access: Custom, meaning that member permissions are set explicitly.
Then expand the members of the sales area hierarchy level and drag North America to the dimension-restricted member area, so that this role's users can only access sales data for the North America region.
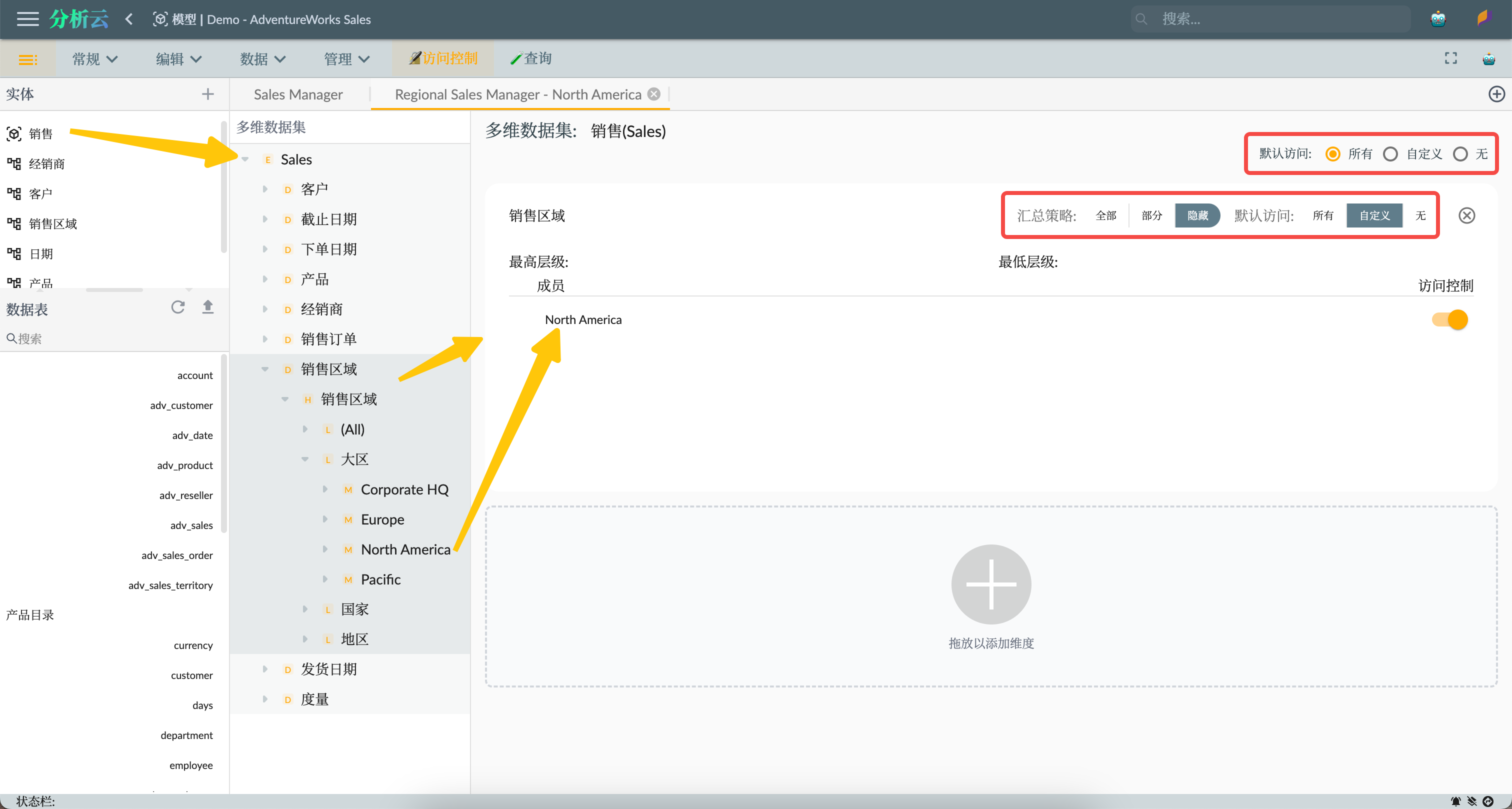
Finally, users assigned to this role will only be able to access sales data for the sales area of North America and its submembers.
Similarly, create a role for the European Regional Sales Manager and set the sales area restriction to Europe.
Product Manager
The Product Manager is a role limited to accessing specific product-related information and cannot access customer dimension information, but can freely access other dimensions.
For example, we create three roles for Product Managers:
- Product Manager
- Product Manager - Bikes
- Product Manager - Clothing
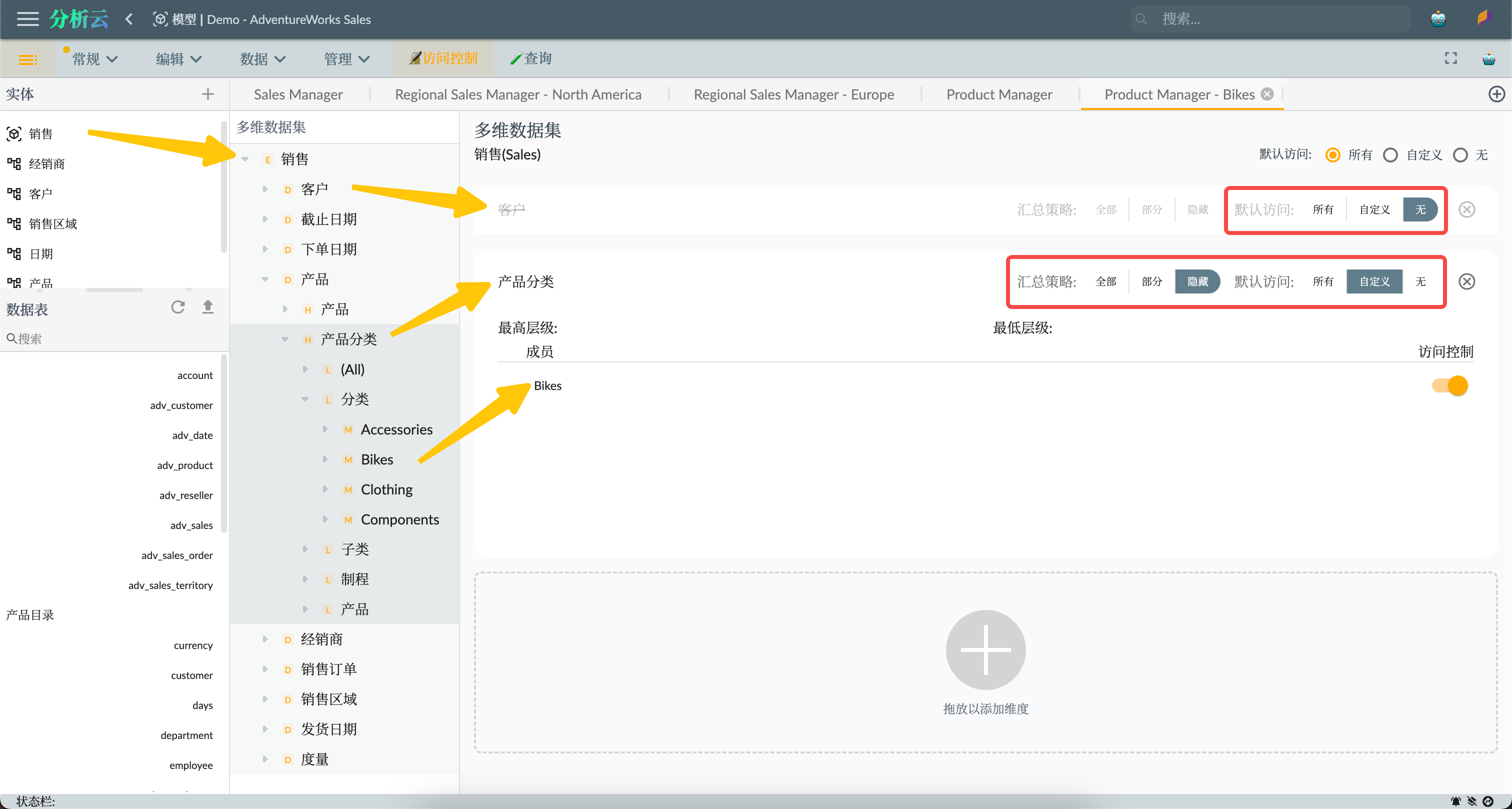
As shown in the figure below, we create the Product Manager - Clothing role, which can only access data for the Clothing member and its submembers in the product dimension, and cannot access customer dimension data:
- Product dimension:
- Consolidation strategy: Hide, which means that access to total data other than allowed members is prohibited.
- Default access: Custom, which means that member permissions are set explicitly.
- Clothing: Allowed access
- Customer dimension:
- Default access: None, which means that access to customer dimension data is prohibited.

The settings for the other two roles are similar, with the Product Manager having access to all data in the product dimension, and the Product Manager - Bikes only able to access data for the Bikes member and its submembers in the product dimension.
Sales Representative
The Sales Representative role has the ability to view sales data, customer information, and sales performance metrics.
For example, we create two roles for sales representatives in two cities:
- Sales Representative - San Francisco
- Sales Representative - London
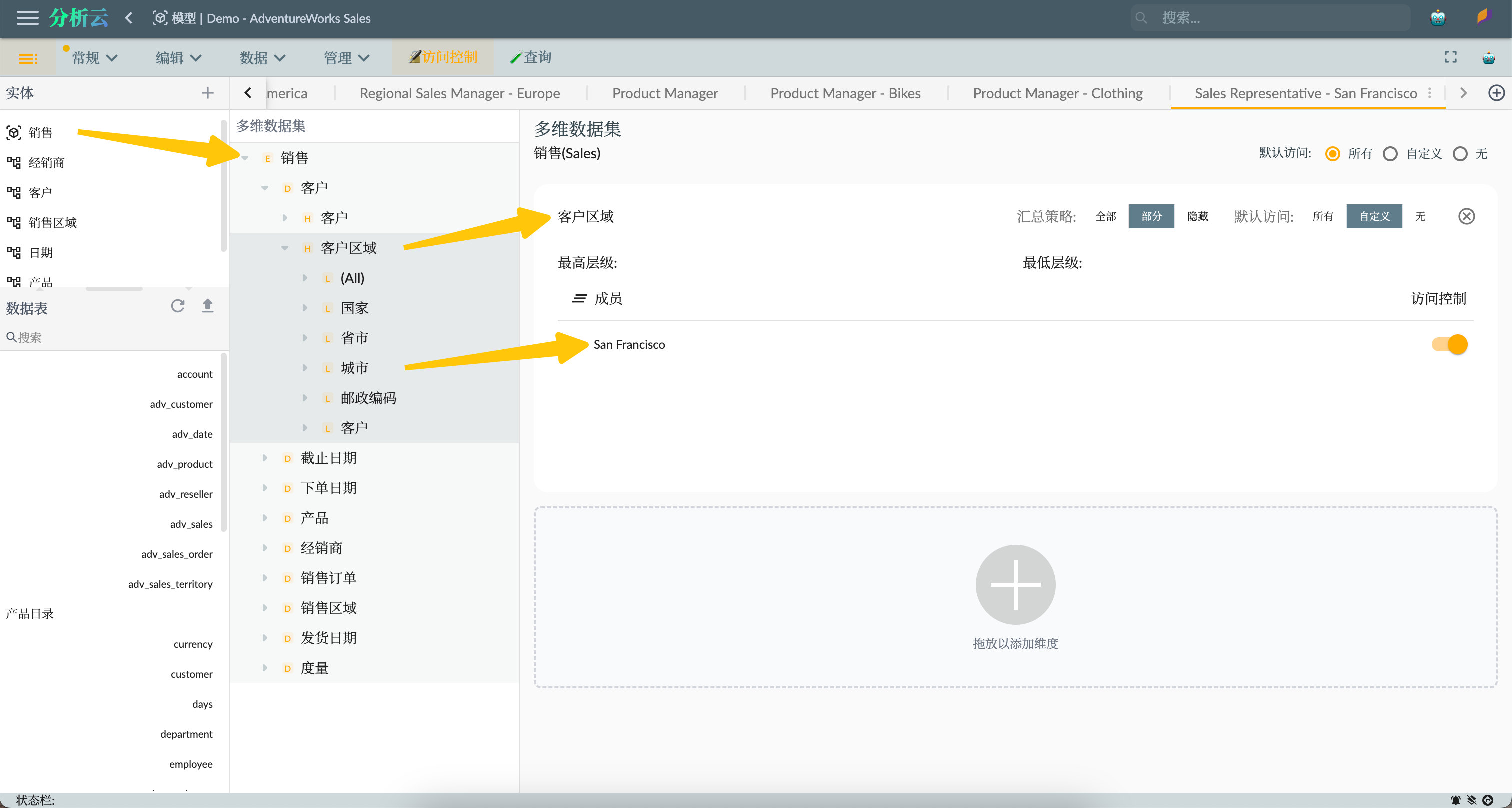
Other sales representatives can be created based on specific customers or larger responsibility areas, such as Germany (Country level) or California (State level).
Composite Roles
Composite Roles are roles composed of multiple roles. They can include other composite roles but cannot include themselves. For example, we can create a composite role that combines the Product Manager and Sales Representative roles, allowing users of this role to access both Product Manager and Sales Representative data.
As shown in the figure below, when creating a composite role, select the type as Composite Role, and then drag the roles to be combined to the right-hand role management area:
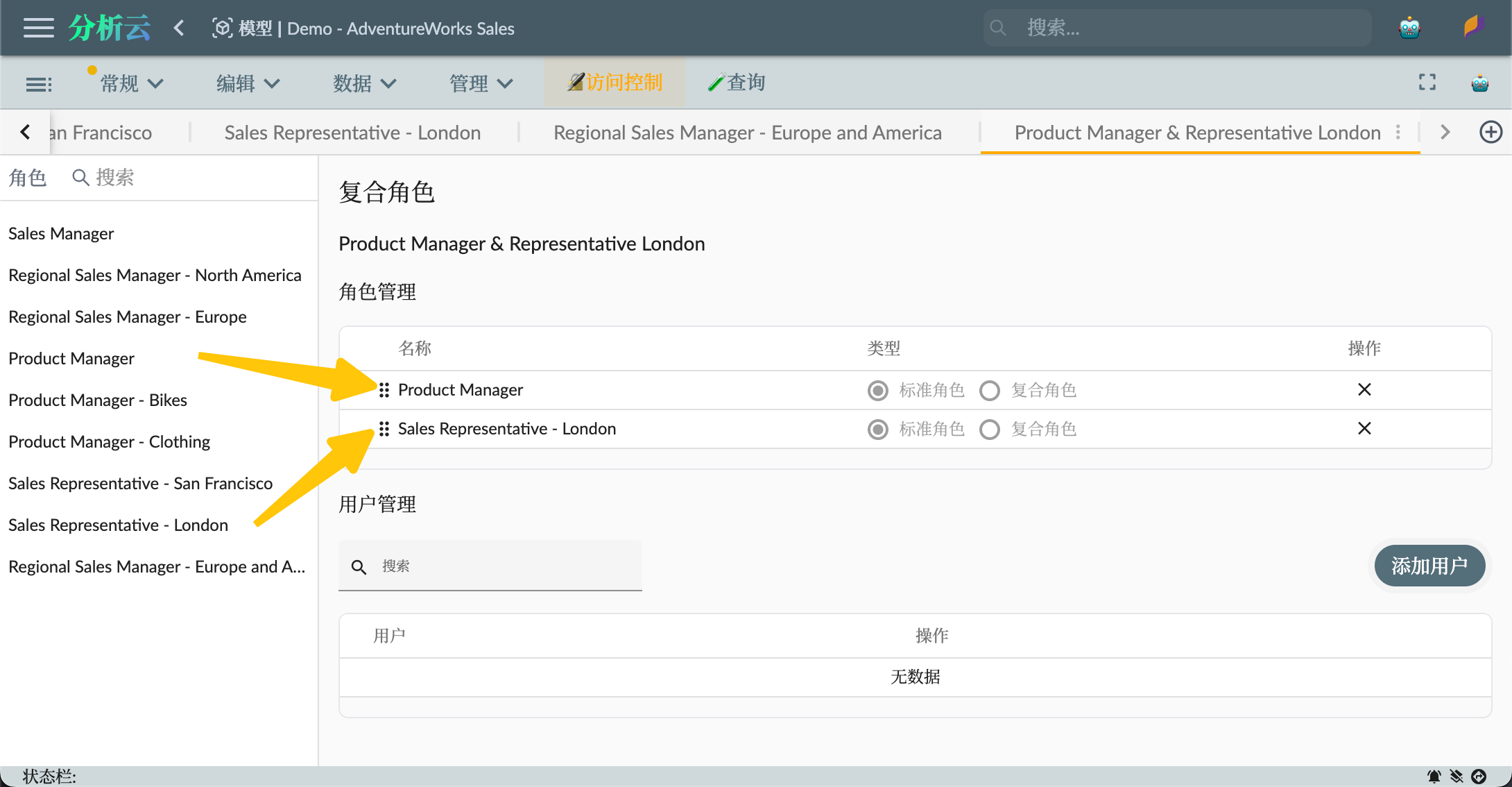
Authorizing Users
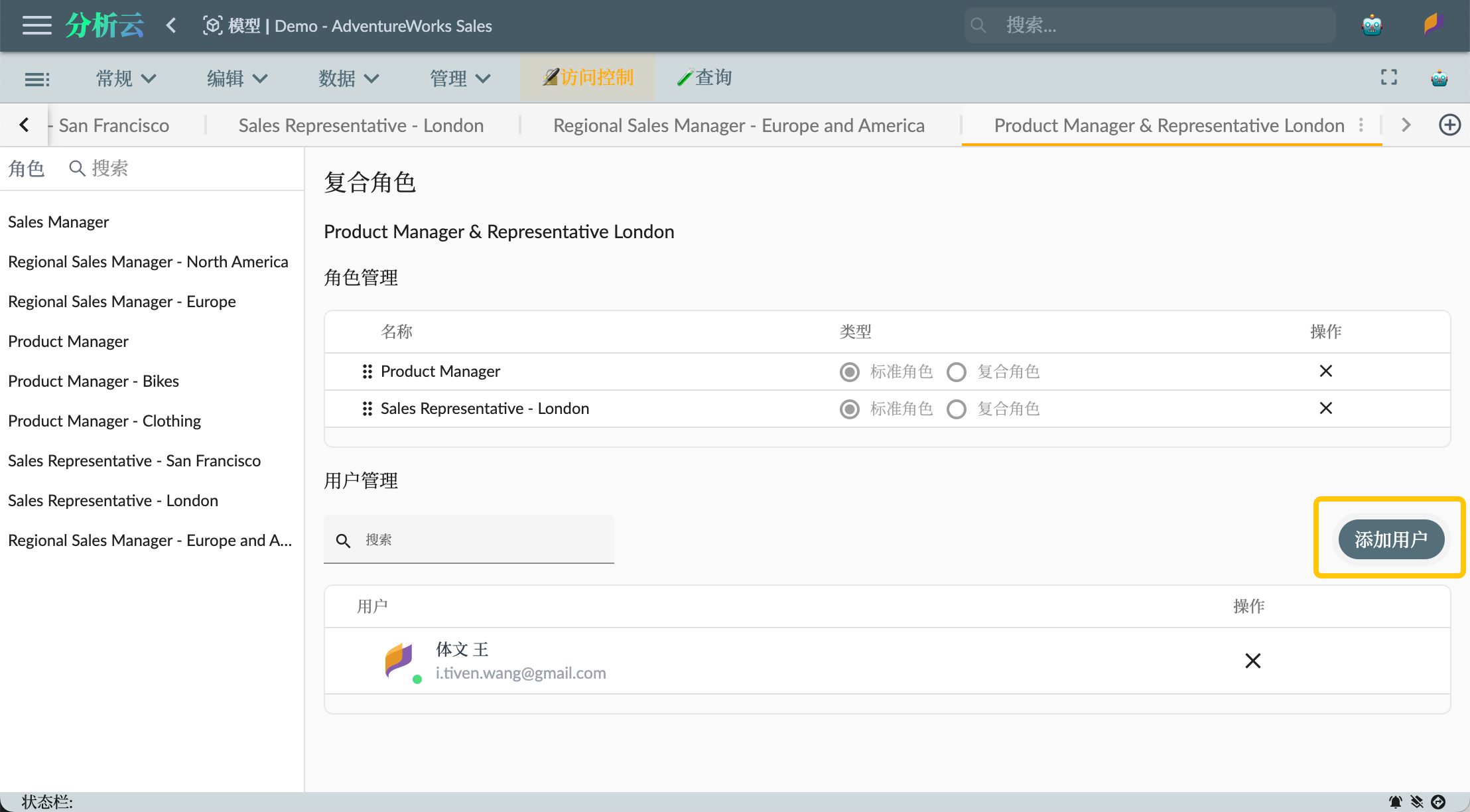
Once roles and permissions are set up, you can authorize users to the respective roles. This can be done by associating users with roles. You can add user accounts to the role's user management to establish the association.
As shown in the figure below, add user accounts in the role's user management to establish the association:
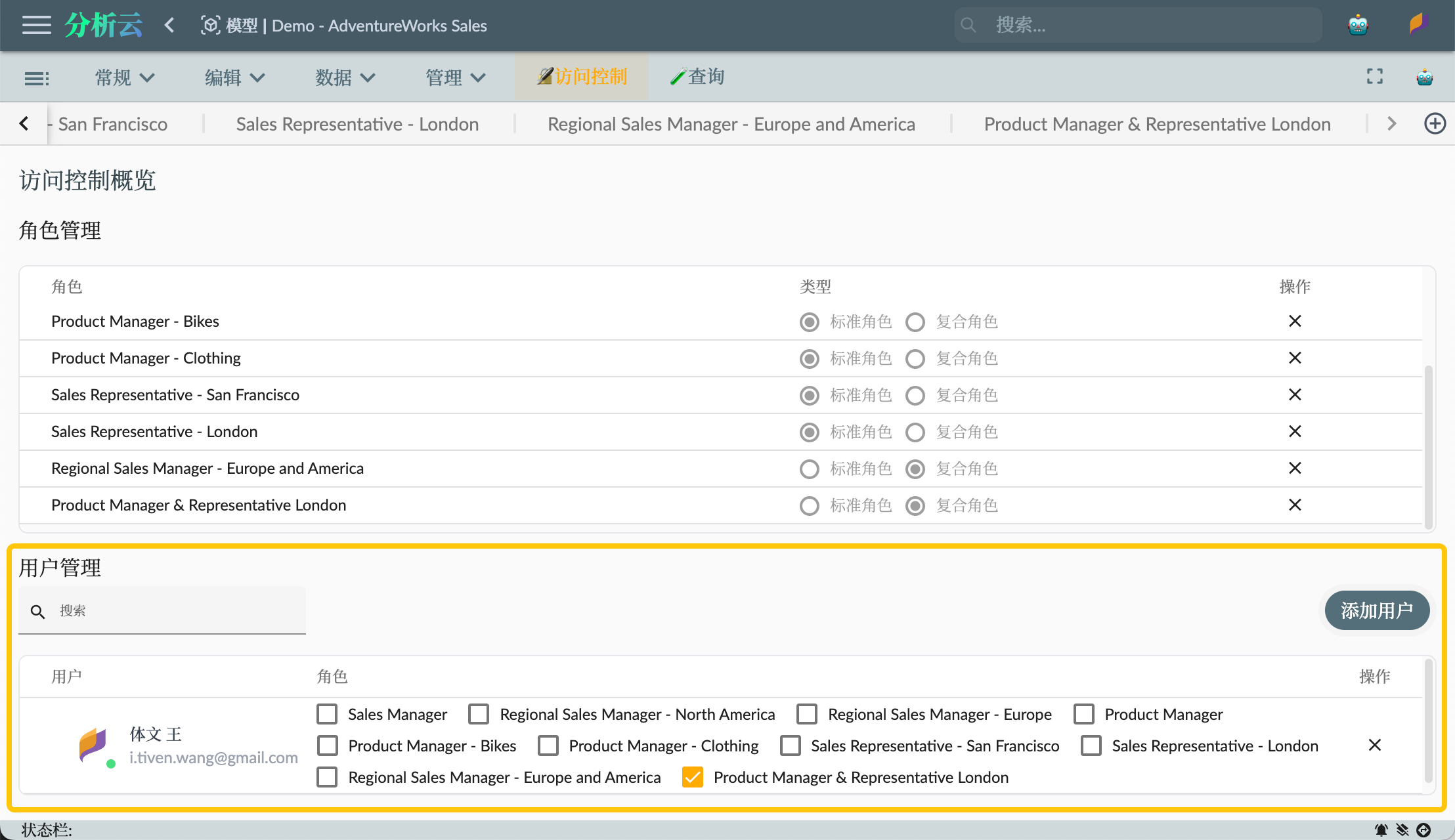
Alternatively, you can add user accounts and assign roles to associate permissions in the user management of the access control overview interface:
Verifying Permissions
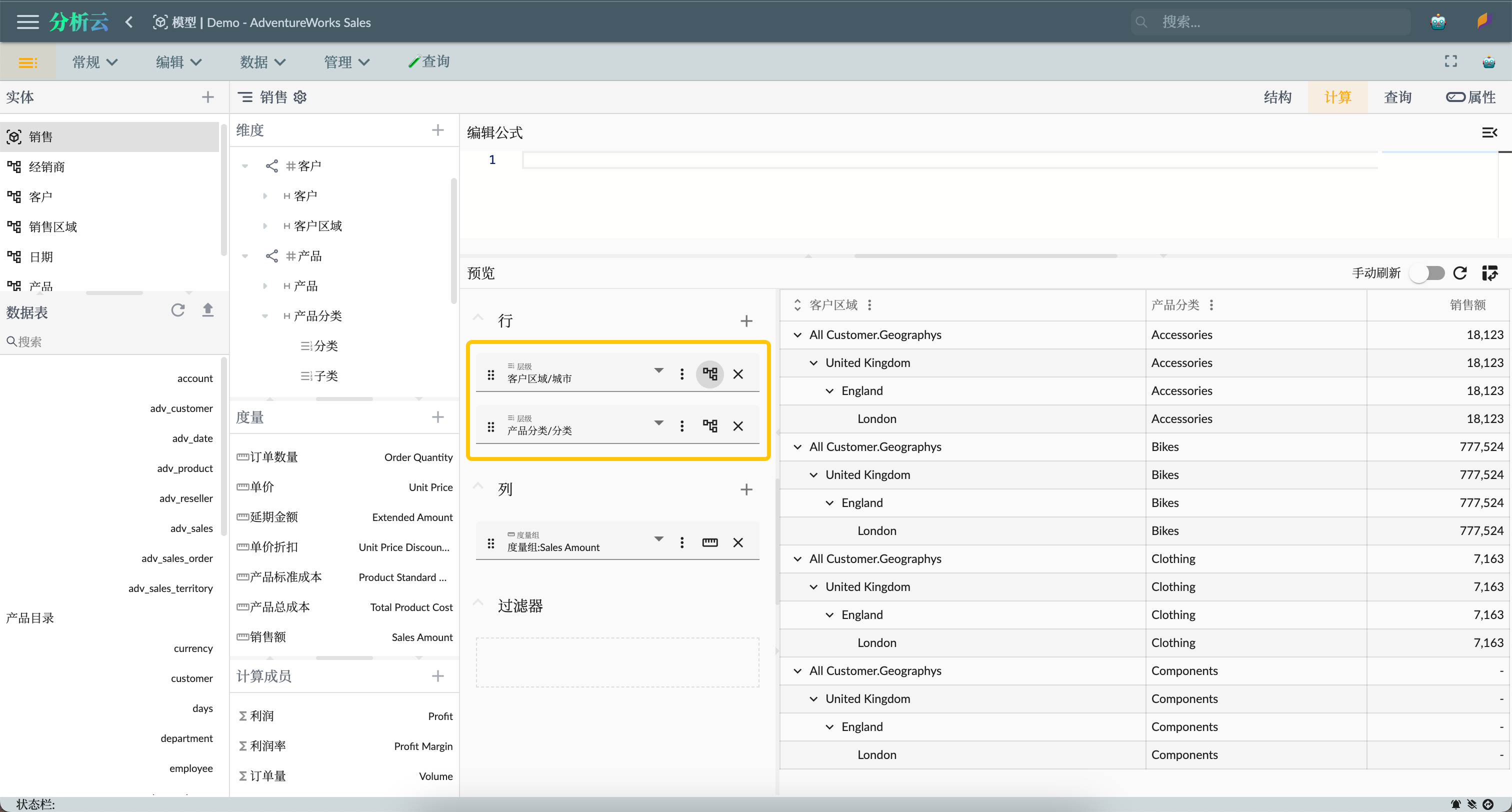
After assigning roles to users, you can verify if the user's permissions are correct. If you are the model editor, you can assign roles to your own account and then go to the multidimensional dataset's computation interface to verify if the data is restricted by role permissions using data preview.
As shown in the figure below, the current account is assigned the Product Manager & Representative London role, so this account can only access customer data for London in the customer dimension and can access all product data in the product dimension:
Conclusion
The semantic model of Xpert Analytics Cloud provides powerful role management and permission control capabilities. Through role management, users can create and define different roles and authorize users to these roles. Each role can have specific data access permissions, including access control to dimensions, levels, and members. Role permissions can be single roles or composite roles, allowing flexible definition of data visibility and operational permissions. In this way, the semantic model of Xpert Analytics Cloud ensures security and data isolation while enabling users to access and operate relevant data based on their role permissions, thereby enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of data analysis and decision-making.