Step 2: Knowledge Pipeline Orchestration
In XpertAI, a knowledge pipeline functions like an intelligent data processing assembly line. Each node performs a specific task, and you can drag, drop, and connect different nodes to gradually transform raw document data into a searchable and understandable knowledge base. The entire process is highly visual and configurable, helping you quickly build knowledge acquisition and indexing flows tailored to your business logic.
This chapter will help you understand the overall flow of the knowledge pipeline, the role and configuration of each node, and how to customize and optimize your knowledge processing chain.
Interface Status Overview
When you enter the knowledge pipeline orchestration interface, you will see:
- Tab Status: The Documents, Retrieval Test, and Settings tabs are grayed out and unavailable.
- Prerequisites: You must complete the configuration, debugging, and publishing of the knowledge pipeline before uploading files and running retrieval tests.
If you choose a blank knowledge pipeline, the system will display a canvas with only the "Knowledge Base Node" by default. You can then follow the guide to create and connect other nodes step by step.
If you select a preset pipeline template, the canvas will immediately show the complete node structure of that template.
Overall Knowledge Pipeline Flow
Before configuring, let's understand how data flows through the knowledge pipeline:
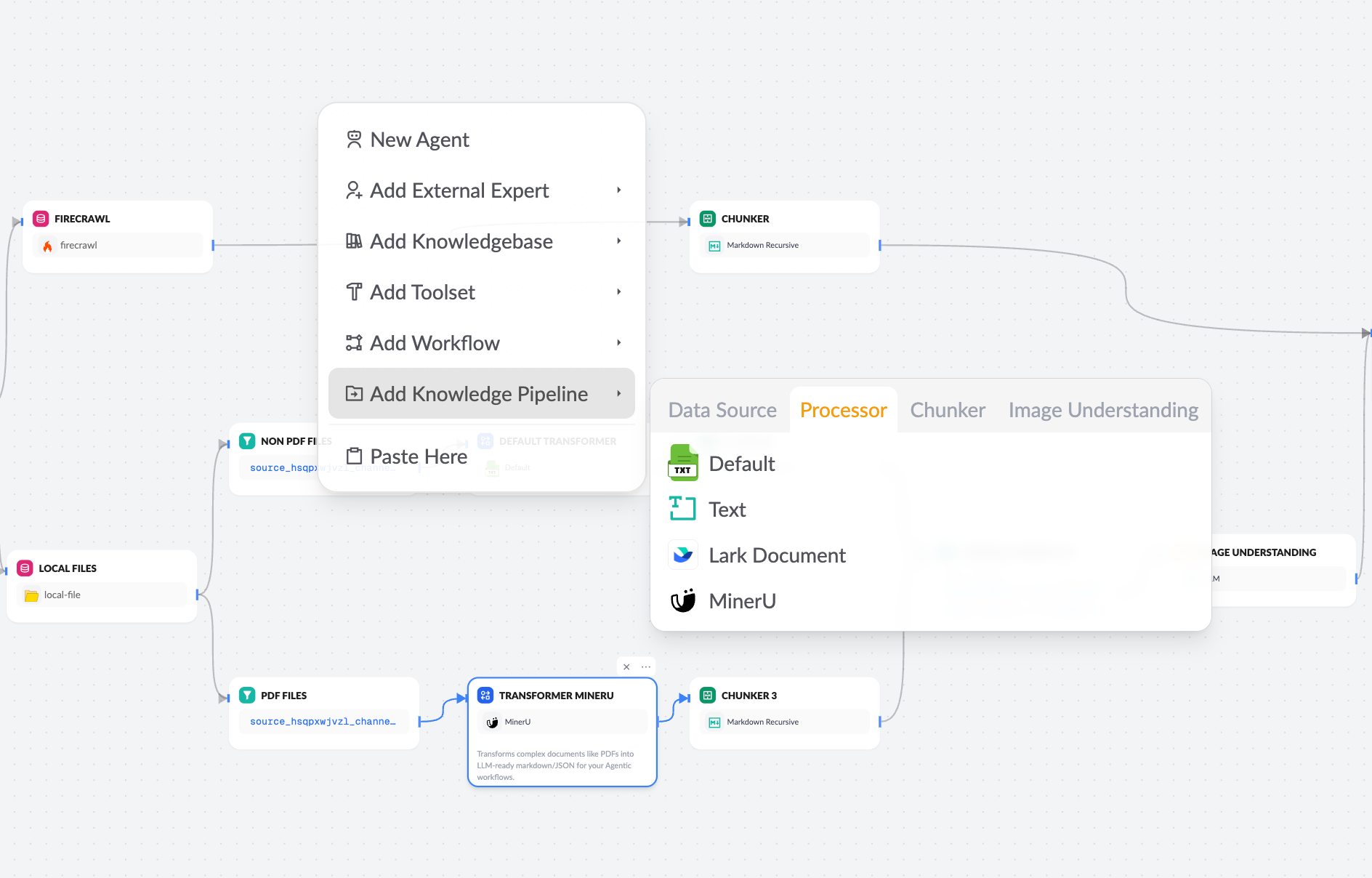
- Data Source Configuration: Import raw content (local files, Notion, web pages, cloud drives, etc.).
- Document Transformer Node: Convert raw files into standardized structured data (supports text and image extraction).
- Chunker Node: Intelligently split structured content into chunks suitable for indexing.
- Knowledge Base Node: Define tree structures and indexing strategies.
- Trigger Node Configuration: Set input parameters to trigger pipeline execution.
- Test & Publish: Validate the process and officially enable the knowledge base.
Step 1: Data Source Configuration
In XpertAI, you can select multiple data sources for knowledge extraction. Each data source can be configured independently and supports local uploads, online documents, and web crawling.
Currently supported data sources include:
- Local file upload
- Online documents (e.g., Notion)
- Cloud drives (Google Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive)
- Web crawlers (Firecrawl, etc.)
More data sources are available via the XpertAI Plugin Marketplace.
Step 2: Configure Data Processing Nodes
Data processing nodes are the core of the knowledge pipeline. They parse, transform, clean, and chunk raw files into structured semantic units. XpertAI divides data processing into two main parts: Document Transformer and Chunker.
Document Transformer
The document transformer converts various file formats (PDF, Word, Excel, etc.) into structured content understandable by models. It supports extraction of images, tables, and text, serving as the "first step" in the knowledge flow.
You can choose the built-in XpertAI transformer or other transformers from the Marketplace (such as Unstructured, MinerU, etc.).
Features
- Supports multiple input formats (PDF, DOCX, XLSX, PPTX, TXT, Markdown, etc.)
- Automatically extracts images and generates usable URLs
- Supports asynchronous tasks and batch conversion
- Supports OCR and structured table extraction
Chunker
After transformation, documents are often too large for direct vectorization and retrieval. The chunker splits content into semantically complete chunks for subsequent indexing and recall.
XpertAI provides multiple chunking strategies, including:
| Type | Features | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| General Chunker | Fixed-size chunks, supports delimiters and overlap | General text |
| Parent-Child Chunker | Automatically generates tree-structured context | Long or complex documents |
| Q&A Processor | Extracts Q&A data, e.g., FAQ or Excel Q&A tables (in development) | Tables or structured Q&A (in development) |
General Chunker
Configuration Options
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Delimiter | Split by line breaks or custom regex |
| Max Length | Automatically splits if exceeded |
| Overlap | Improves context association |
Input/Output
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Input | Document | Raw text content |
| Output | Document with chunks | Array of semantic chunks |
Parent-Child Chunker
The parent-child chunker generates a tree-structured chunk tree, a unique XpertAI chunking system that manages hierarchical relationships between parent and child chunks.
Unlike traditional "chunk structures," XpertAI uses a tree structure to store chunks, supporting multi-level traceability and aggregation.
Features
- Automatically maintains context association
- Supports semantic retrieval at parent level and precise matching at child level
- Can be extended to a hybrid graph structure
Q&A Processor — In Development
The Q&A processor combines extraction and chunking, used to extract Q&A pairs from CSV or Excel files. This node is under development and will support batch processing of structured Q&A knowledge.
Step 3: Configure Knowledge Base Node
The knowledge base node is the endpoint of the pipeline, responsible for building a searchable knowledge index structure.
XpertAI's knowledge base uses a tree-structured chunk system to manage chunk hierarchies. Each node (chunk) can be associated with vectors, images, source information, and context nodes.
Core Features
| Module | Description |
|---|---|
| Structure | Unified tree-structured chunking |
| Indexing | Vector index |
| Retrieval | Semantic similarity-based recall |
| Keyword Index | In development, hybrid retrieval |
Step 4: Configure Trigger Node (User Input Parameters)
In XpertAI, user input parameters are managed via the Trigger Node.
The trigger node lets you define runtime input parameters (such as file upload, URL, delimiter, custom variables, etc.), which are injected into upstream nodes during execution.
Advantages
- Unified parameter management
- Automatic binding with other nodes
- Visual configuration and default value support
Step 5: Test & Publish
After configuring the pipeline, click the Test Run button in the upper right to validate the entire process. The system will execute each node in sequence and output the final knowledge base result.
Once testing passes, click Publish to officially apply the knowledge pipeline to your knowledge base.
Summary
XpertAI's knowledge pipeline integrates data processing, chunk management, and index building into a unified architecture:
Trigger (Runtime Inputs) → Data Source → Document Transformer
→ Chunker (Tree Structure)
→ Image Understanding (vlm/ocr)
→ Knowledgebase (Vector Embedding)
This system not only simplifies knowledge base construction but also ensures cross-document consistency, context traceability, and maximized retrieval performance.